Java程序访问数据库
发布时间:2020-03-10
修改时间:2025-04-18
阅读次数:2391
一、JDBC概述
JDBC(Java Database Connectivity)是一种用于执行SQL语句的Java API,由一组类与接口组成,通过调用这些类和接口所提供的方法,可以使用标准的SQL语言访问数据库。
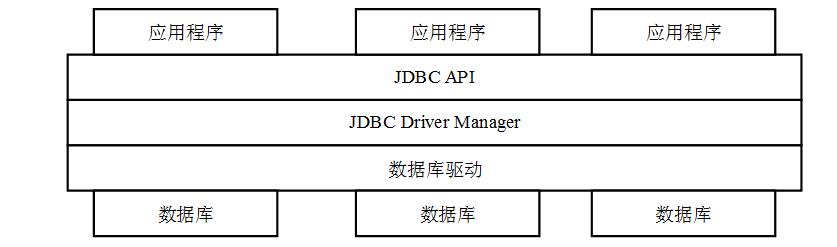
二、访问数据库流程
首先下载mysql数据库的驱动jar包(mysql 5.x),添加到工程classPath下(拷贝到工程目录-右击-Build Path-Add to BuildPath)。
(1)加载驱动。
(2)创建连接对象。
(3)创建语句对象。
(4)调用语句对象的方法执行SQL语句。
(5)如果执行的是查询语句,处理返回结果。
(6)释放资源(结果集,语句、连接对象)。
三、示例
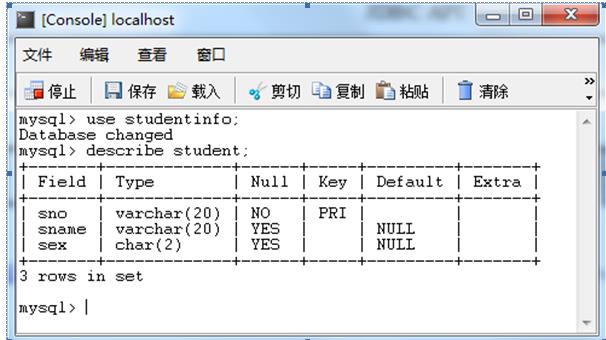
1、表结构:
2、代码
(1)添加记录
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");// 加载驱动
String url = "jdbc:mysql:///studentinfo"; // 连接字符串
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "sa");// 连接数据库
// 执行语句1
String sql1 = "insert into student values(?,?,?)";// 准备sql语句,?是占位符,内容待定
PreparedStatement pst1 = con.prepareStatement(sql1);// 创建封装语句的对象
pst1.setString(1, "20175678");// 给第1个占位符赋值
pst1.setString(2, "李四");// 给第2个占位符赋值
pst1.setString(3, "男");// 给第3个占位符赋值
pst1.executeUpdate();// 执行sql语句1
pst1.close();// 关闭语句对象,写到这执行一下,看记录是否添加到数据库中
con.close();
}
}(2)查询记录
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");// 加载驱动
String url = "jdbc:mysql:///studentinfo"; // 连接字符串
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "sa");// 连接数据库
// 执行查询语句
String sql2 = "select * from student";// 准备sql语句
PreparedStatement pst2 = con.prepareStatement(sql2);// 创建封装语句的对象
ResultSet rs = pst2.executeQuery();// 查询结果返回到ResultSet中
while (rs.next()) {// 利用循环输出ResultSet中的内容
System.out.println(rs.getString(1) + "," + rs.getString(2) + "," + rs.getString(3));// 1,2,3分别代表第1,2,3列
}
rs.close();// 关闭结果集
pst2.close();// 执行sql语句1
con.close();// 关闭连接
}
}(3)批量删除记录
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");// 加载驱动
String url = "jdbc:mysql:///studentinfo"; // 连接字符串
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "sa");// 连接数据库
String sql3 = "delete from student where sno=?";// 准备删除语句
String[] snos= {"111","222","333","444"};//要删除的学号
PreparedStatement pst3 = con.prepareStatement(sql3);// 创建封装语句的对象
for(String sno:snos) {
pst3.setString(1, sno);
pst3.addBatch();
}
pst3.executeBatch();//批量删除
pst3.close();// 执行sql语句1
con.close();// 关闭连接
}
}(4)对事务的支持
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");// 加载驱动
String url = "jdbc:mysql:///studentinfo"; // 连接字符串
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "sa");// 连接数据库
PreparedStatement pst1 = null;
con.setAutoCommit(false);
// 执行语句1
String sql1 = "insert into student values(?,?,?)";// 准备sql语句,?是占位符,内容待定
pst1 = con.prepareStatement(sql1);// 创建封装语句的对象
pst1.setString(1, "20179999");// 给第1个占位符赋值
pst1.setString(2, "李四");// 给第2个占位符赋值
pst1.setString(3, "男");// 给第3个占位符赋值
pst1.executeUpdate();// 执行sql语句1
int a = 10 / 0;
con.commit();
pst1.close();
con.close();
}
}20行语句发生异常,事务会回滚,记录添加不成功,尝试将11,21行去掉会怎样。
4、封装
我们通常把数据库的操作封装到一个Dao类中,每个基本操作对应一个方法,以表student为例。
(1)在源文件目录src下建立属性文件db.properties存放数据库连接信息(驱动路径,连接字符串、用户名、密码等)。
(2)建立工具类JdbcUtil.java封装获取连接和释放资源的方法。
(3)建立和表对应的实体类。
(4)建立Dao类封装表的增删改查方法。
5、测试
对Dao类的多个方法进行测试,可以引入junit框架,比直接在main方法中测试方便。需要将junit的jar包引入工程。引入方法:将jar包拷贝到工程下,并添加到BuildPath下。代码如下。测试方法:在右侧OutLine区右击要测试的方法-Run as JUnit Test。
package test;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import dao.StudentDao;
import entity.Student;
public class StudentDaoTest {
StudentDao studentDao=new StudentDao();
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
}
@Test
public void testAdd() throws Exception{
Student student=new Student("20180001","张三","男");
studentDao.add(student);
}
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws Exception{
Student student=new Student("20180001","张三","女");
studentDao.update(student);
}
@Test
public void testDelete() throws Exception {
studentDao.delete("20180001");
}
@Test
public void testFindById() throws Exception{
Student student=studentDao.findById("20180001");
System.out.println(student.getSname());
}
@Test
public void testQuery() throws Exception{
List<Student> studentList=studentDao.query();
for(Student student:studentList) {
System.out.println(student);
}
}
}